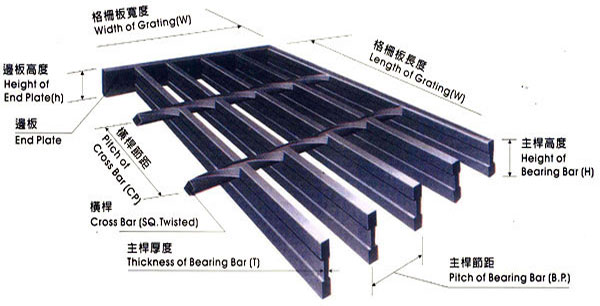
I-Shape Steel Grating is used where high strength is required and light weight is critical with saving materials and more economical, perfect appearance.
I-Shape Steel Grating Features:
I Type Steel Grating,Compound Plain I Type Steel Grating,I Type Steel Bar Grating,Plain Type Steel Grating Hebei Zhenxing Jinyuan Wire Mesh Group Co.,Ltd , https://www.zxsteelgrating.com
/*728*90 created on 2018/5/16*/ var cpro_id = "u3440131"; Home>Bearing knowledge>Thrust ball bearing terminology Thrust ball bearing terminology
Calibration of bearing clearance: 1. Calibration of the bearing unit clearance, 2. The clearance of the bearing mounted on the shaft or adapter sleeve is calibrated to the minimum and maximum filler: 1. The standard clearance is C02. When using the calibration clearance; modify 3 with the modification of the above table. The modified value of the C2 clearance is different between the maximum and the minimum; the original radial clearance of the rolling bearing is not to be misused as: the inner ring is radially from one pole to the other with respect to the outer ring when the device is not subjected to radial force. The working clearance of the pole bearing is defined as: after the device; the amount of movement of the shaft in the radial direction relative to the bearing outer ring without load; the working clearance is the original radial clearance minus the interference due to the interference and heating The amount of change in clearance caused by expansion ΔS (in μm units)-----Can rolling bearings be okay, the degree of function is absolutely determined by the decision on whether or not the appropriate job clearance can be reached. The original clearance is selected by the tolerance together and the effect of temperature is determined /*250*250 was created on 2017/12/25*/ var cpro_id = 'u3171089';
---Selection of bearing clearance--Selected reference for radial internal clearance:
Theoretically; the play in the bearing work is only negative; the lifespan becomes the longest; but we all know that even if the negative negative clearance is larger than this, it will agilely reduce the life. Usually the initial clearance is larger than 0. Most of the miniature bearings and small-aperture bearings are selected for MC3; usually the bearing is selected C0
The wheels in the table are all axially loaded with axial load and do not preload axially; do not want to reduce the clearance; want to reduce the clearance and want to control the oscillation and the acoustic low-speed revolving zigzag want to reduce the collision torque common axial load common axial Rigid inner wheels are only tight together; outer wheel clearance together with low and medium speed turns and twists uniquely want to reduce conflicting torque axial load, generally axial rigid heavy load, impact load; demand interference inner wheel high temperature or outer wheel low temperature; shaft twist Big
--- Measure the radial clearance of the bearing to pay attention to accidents: (1) can use the special instrument measurement method, (2) use the hand push method to measure the demand measurement, the measurement skills have higher measurement skills. When the clearance is at the edge; the error is simple; at this moment; the instrument measurement shall prevail, (3) when measuring the thickness gauge; it shall be operated according to the standard rules; without applying the roller, the roller is rolled from the thickness gauge. Method measurement; (4) During the measurement process, ensure that the ball falls into the bottom of the groove; closed bearings are measured before closing; when using a loaded instrument, the measured value should also be reduced by the amount of clearance caused by the load (5) Multi-row bearing; required for each column clearance; take the arithmetic equivalent of each column as the radial clearance of the bearing
--- Bearing static load bearing dynamic load: static load bag pregnancy does not change the dead load (such as self-weight) at any time and the loading change is slow so that the quasi-static load can be omitted, the dynamic load bag pregnancy The impact load of the speed effect (such as air hammer), the periodic load that changes periodically at any time (such as the air compressor of the air compressor) and the random load of the non-period change Cr are the fixed dynamic load, which is the maximum in the transition case. Load capacity, the unit is KN; Co is a fixed static load. It is the load capacity that does not change; these two are the basic fixed dynamic load C calculated by the radial load used to calculate the bearing under dynamic stress; that is, a bearing that changes under load, the value implies that according to ISO281: 1990 standard; bearing load of 1 million revolutions of base fixed life assumes that the load size and target intention are unchanged; radial load for radial bearings; axial load for intermediate thrust bearings
---Axial load: Intended load along the axis of the bearing. Radial load: The intended load bearing perpendicular to the axis is the bearing oscillation (lifting rate) is divided into Z, Z1, Z2, Z34 grades, bearing oscillation (rate) Divided into V, V1, V2, V34 grades
The Z and V grades are used for the bearing manufacturer to check the deep groove ball bearing oscillation in the standard rule planning. The Z1 and V1 grades are used to check the bearing products with normal requirements for bearing oscillation. The Z2 and V2 grades are used for Y series electromechanical and Other electromechanical bearings for the corresponding requirements; Z3, V3 grades are used in the international advanced level when there is a strict demand for oscillation.
Recommend to friends comments close window Bearing related knowledge SKF bearing calibratable bearing life types and basic concepts bearing terminology in English -7
Option to purchase imported bearings
Calibration of SKF bearing alignment function
The key to NSK bearing cooperation
This article links to http://
Please indicate China Bearing Network http://
Previous:Installation method of plane thrust bearing loose ring Next:Ceramic bearing
1) China: YB / T4001 - 1998
2) USA: ANSI / NAAMM (MBG531 - 88 )
3) UK: BS4592 - 1987
4) Australia: AS1657 - 1985


Source: Bearing network time: 2013-12-05